Breast augmentation is one of the most sought-after cosmetic procedures globally, offering women the ability to enhance their breast volume after pregnancy or weight loss and correct asymmetry.
At MACS Clinic, Watford, the procedure is performed by Mr. Shailesh Vadodaria, a senior consultant plastic surgeon. This procedure is carefully planned and personalised for each patient to achieve natural and safe, results.
This blog outlines all the essential aspects of breast augmentation surgery offered at MACS Clinic, including implant options, surgical approaches, complications, and long-term considerations.

1. Types of Breast Implants
At MACS Clinic, the choice of breast implant is based on your goals, body type, and surgical plan. The two primary types of implants include:
A) Silicone Gel Implants
- Filled with cohesive silicone gel that closely mimics natural breast tissue.
- Preferred for their soft, realistic feel.
- Lower risk of visible rippling or wrinkling.
- Available in various firmness levels (standard, soft-touch, high-cohesive).
- Require a slightly longer incision.
B) Saline Implants
- Filled with sterile saltwater solution, either pre-filled or inflated during surgery.
- Can be inserted through smaller incisions.
- In the event of rupture, the body naturally absorbs the saline.
- May feel less natural and show more rippling, particularly in thinner patients.
- Less commonly used in the UK.
All implants used at MACS Clinic are CE-marked and meet UK and European safety standards.
2. Shapes of Breast Implants
Choosing the right shape is crucial for achieving a desired result.
A) Round Implants
- Symmetrical and provide enhanced upper pole fullness.
- Suitable for patients seeking a more prominent cleavage.
- Maintain shape even if they rotate.
B) Teardrop (Anatomical) Implants
- Shaped like a natural breast, with more volume at the bottom.
- Create a subtle, natural-looking contour.
- Require precise placement to avoid visible rotation.
- If it rotates in the breast then it causes change in the shape of breast
3. Planes of Implant Insertion
The plane refers to where the implant is placed in relation to your chest muscle (pectoralis major) and breast tissue.
A) Subglandular (Above the Muscle)
- Placed between the breast tissue and the chest muscle.
- Less discomfort post-surgery.
- Suitable for patients with sufficient natural breast tissue.
B) Submuscular (Below the Muscle)
- Positioned beneath the pectoralis muscle.
- Offers a more natural appearance in patients with less breast tissue.
- Decreased risk of rippling and capsular contracture.
- Longer recovery due to more tissue manipulation.
C) Dual Plane
- Implant is partly under the muscle and partly under the glandular tissue.
- Combines benefits of both placements.
- Often recommended for patients with mild breast droop (ptosis).
- Limitations of Breast Implants
Breast augmentation is transformative, but it is essential to understand its limitations:
- Not a solution for breast sagging: A breast lift (mastopexy) may be needed in conjunction.
- Not permanent: Implants generally last 10–15 years before potential replacement or revision.
- Breastfeeding: Usually possible but not guaranteed.
- Impact on mammograms: May obscure imaging; special techniques are used.
- Aging, pregnancy, weight changes: Can affect long-term results.
Reasons Why Women Choose Breast Augmentation
1. Enhancement of Small or Underdeveloped Breasts
Many women feel that their natural breast size is disproportionate to their body frame. Augmentation helps achieve a fuller breast contour, improving body balance.
2. Correction of Breast Asymmetry
It is very common for one breast to be slightly larger or differently shaped than the other. Implants can restore symmetry, which can make clothing fit better and boost self-confidence.
3. Post-Pregnancy or Weight Loss Changes
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and significant weight loss can lead to volume loss and sagging. Augmentation can help restore the lost volume, often in combination with a breast lift.
4. Reconstruction After Mastectomy
Breast cancer survivors often undergo breast augmentation or reconstruction after mastectomy to regain their body image and femininity.
5. Gender Affirmation Surgery
Breast augmentation is an important step for many transgender women as part of their gender-affirming journey, helping align physical appearance with gender identity.
6. Boost in Confidence and Femininity
Many women feel more feminine, attractive, and empowered after enhancing their breast size, which can positively impact their self-esteem and body image.
7. Clothing Fit and Social Comfort
Better fitting clothes, swimwear, and lingerie can lead to improved confidence in social situations and professional settings.
Impact of Breast Augmentation:
Following observations are reported and claimed patients :
Positive Impacts
- Improved Body Image: Most women report feeling more positive about their bodies after surgery.
- Enhanced Self-Esteem: A fuller, proportionate bust line can translate into greater self-worth and emotional well-being.
- Better Intimacy and Relationships: Some women experience improved intimacy and confidence in personal relationships.
- Professional Confidence: An improved self-image often leads to greater assertiveness and confidence in work or social environments.
- Psychological Empowerment: Regaining control over one’s body can be empowering, especially for women who underwent physical trauma or cancer treatment.
Potential Psychological Considerations
- Unrealistic Expectations: If the patient expects perfection or views surgery as a solution to deep-seated insecurities, results may not bring long-term happiness.
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD): Women with BDD may continue to feel dissatisfied even after successful surgery. A psychological evaluation may be recommended in such cases.
- Adjustment Period: It may take weeks or months to fully adjust to the new appearance, and emotional reactions can vary from person to person.
Social and Cultural Influences
- Media and Celebrity Culture: Idealised body images on social media and in pop culture often influence personal beauty standards.
- Partner Preferences: While not always the primary reason, some women may be influenced by their partner’s or peer group’s opinions.

Breast Augmentation procedure at MACS Clinic
Initial Consultation
Steps for Booking a Consultation with Mr. Shailesh Vadodaria at MACS Clinic
Contact the Clinic:
- Phone: Call the clinic at 020 7078 4378.
- WhatsApp: Message the clinic at 07792 648 726.
- Email: Send an email to enquiries@macsclinic.co.uk.
- Online booking using our calendly: https://calendly.com/macsclinic/free-video-consultation
MACS clinic staff will respond to your inquiry and offer you a complimentary video or face-to-face consultation with Mr. Shailesh Vadodaria, the senior consultant plastic surgeon.
You will be provided with a detailed information factsheet about breast augmentation procedure to give you better insight into what to expect.
Consultation with Mr. Vadodaria:
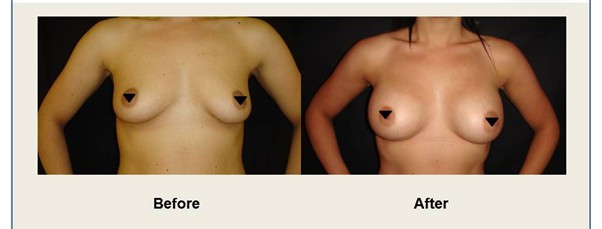
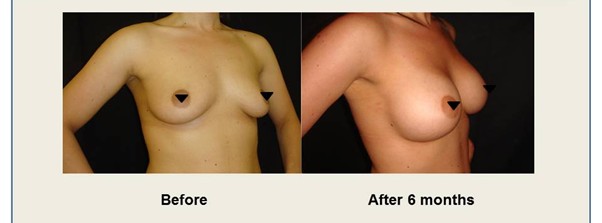
During your consultation, Mr. Vadodaria will thoroughly explain all aspects of the breast augmentation procedure, including potential risks, complications, and post-operative care. Mr Vadodaria will also discuss implant options — type (silicone or saline), shape (round or anatomical), size, and surface texture. He will also present representative before and after photos/videos of previous breast augmentation patients from his practice.
Pre-Operative Preparation
After the consultation, the MACS Clinic team will send you a procedure estimate to help you plan accordingly. These prices may vary based on factors such as the type of anaesthetics used and your choice of clinic or hospital. Following your consultation with Mr. Vadodaria, a final cost estimate will be provided to you.
Preparation for the procedure:
Upon arrival at MACS clinic, you will need to complete the consent process. This ensures that you fully understand the treatment, its potential risks, and the expected outcomes. In compliance with National Government Law, a pregnancy test will be conducted to ensure patient safety.
Surgical Procedure (Step-by-Step)
Duration: Approx. 60 to 90 minutes
Anaesthesia: General anaesthetic (you will be asleep)
Step 1: Incision
One of the following incisions is made based on your anatomy and implant choice:
- Inframammary: In the breast crease (most commonly used, well-hidden).
- Periareolar: Around the edge of the nipple (used selectively).
- Transaxillary: In the armpit (less common).
Step 2: Implant Pocket Creation
Mr. Vadodaria creates a space or “pocket” to insert the implant. This pocket may be:
- Subglandular (over the muscle)
- Submuscular (under the pectoral muscle)
- Dual-plane (partially under the muscle)
Step 3: Implant Placement
The chosen implant (filled with silicone or saline) is inserted into the pocket and adjusted to achieve symmetry and natural positioning.
Step 4: Closing the Incisions
Multiple layers of dissolvable sutures are used to close the incisions. Skin adhesive or surgical tape may be applied for extra support.
Step 5: Dressings & Support Bra
Sterile dressings are placed over the incision, and a surgical bra or compression garment is fitted to minimise swelling and support healing.
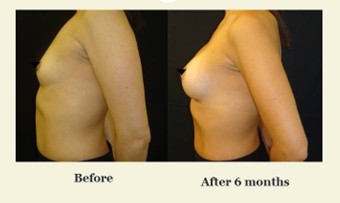


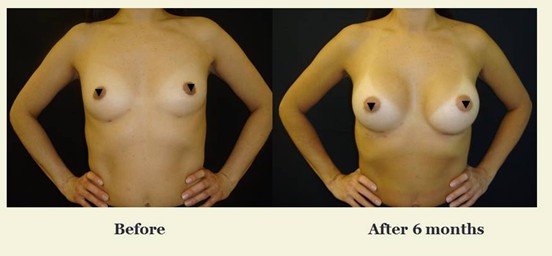

Recovery Process
Immediate Post-Surgery:
- You will be monitored in recovery for a few hours.
- Pain is usually managed with oral painkillers and analgesics.
You can typically go home the same day or after one night’s stay.
Recovery Timeline:
Time Frame What to Expect
- First 3–5 – Days Mild swelling, soreness, and tightness; light activities only
- 1 Week – Sutures dissolve; you may return to work (desk job)
- 2–3 Weeks – Gradually resume normal activities; avoid heavy lifting
- 4–6 Weeks – Resume gym, high-impact exercise (as advised)
- 3–6 Months – Final shape settles, scars begin to fade
Mr Vadodaria will provide clear aftercare instructions, including how to manage swelling, sleeping positions, scar care, and signs of complications to watch for.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any surgery, breast augmentation carries risks, though they are rare:
- Bleeding, infection, or delayed wound healing
- Capsular contracture (hardening of scar tissue around the implant)
- Implant rupture or leakage
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation
- Asymmetry or implant malposition
- Rare conditions: BIA-ALCL or implant-associated illness . All our patients are expected to make an informed choice after going through in details all the possible complications associated with breast implants before making an informed choice .
- Palpability of the edge of the implants
All patients are informed, monitored, and followed up regularly to minimise risks.
Follow-Up and Long-Term Care
Follow-up appointments at 1 week, 6 weeks, 3 months, and 1 year post-operatively.
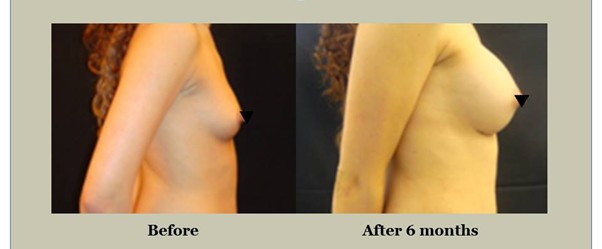
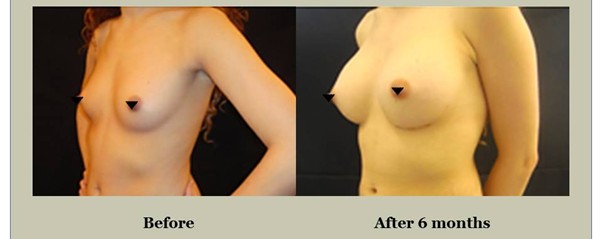

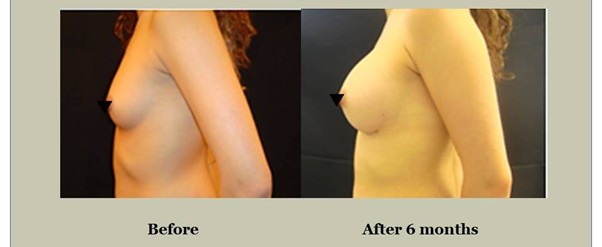
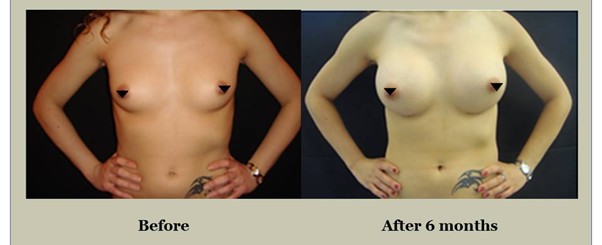
Alternative Methods for Breast Augmentation
For patients seeking non-implant options, MACS Clinic offers:
Fat Transfer Breast Augmentation
- Fat is harvested from areas like the abdomen or thighs via liposuction.
- Purified and re-injected into the breasts.
- Ideal for modest enhancement (up to one cup size).
- No foreign material used — natural look and feel.
- Results may vary due to fat absorption over time.
Breast Implant-Associated Illness (BII)
Breast Implant Illness is a term used by some women to describe a variety of systemic symptoms they believe are related to their implants. These symptoms may include:
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Muscle pain
- Hair loss
- Depression or anxiety
While medical research has not established a definitive link between implants and these symptoms, MACS Clinic acknowledges and respects patient concerns. We offer supportive consultations and implant removal (explantation) with or without en bloc capsulectomy when appropriate.
Breast Implant-Associated ALCL and SCC
1. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL)
- A rare, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma linked primarily to textured implants.
- Occurs in the capsule surrounding the implant, not in breast tissue.
- May present as swelling, a fluid-filled seroma, or a mass years after surgery.
- Incidence: Approximately 1 in 20,000 to 1 in 80,000.
- Diagnosis: Ultrasound, MRI, fluid aspiration, and CD30 testing.
- Treatment: Implant and complete capsule removal.
MACS Clinic no longer uses textured implants and continues to monitor all patients with prior textured devices.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) in the Implant Capsule
- Extremely rare.
- Arises from chronic inflammation in the implant capsule.
- Research is ongoing to understand pathophysiology and risk.
MACS Clinic supports regular follow-ups and offers imaging for any late-onset symptoms related to implants.
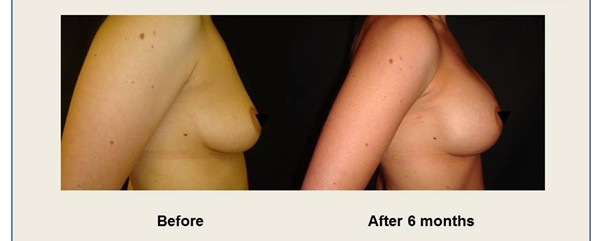


Contact us:
- Phone: 020 7078 4378
- WhatsApp: 07792 648 726
- Email: enquiries@macsclinic.co.uk
- Website: www.macsclinic.co.uk
- BOOK a FREE Video Consultation: https://calendly.com/macsclinic/free-video-consultation?month=2025-01